Obsolete BGP Attributes in the LACNIC Region
January 28, 2025

By Guillermo Pereyra, Security Analyst, and Elisa Peirano, R&D Data Analyst, at LACNIC
In 2023, numerous BGP sessions were shut down because of the presence of obsolete attributes in BGP announcements. This incident, which affected the connectivity of several autonomous systems (AS), highlighted the importance of maintaining a robust and up-to-date routing infrastructure.
What Are BGP Attributes?
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is essential for the operation of the Internet, as it allows Autonomous Systems to exchange routing information. BGP UPDATE messages play a key role in this process, as they announce new routes, modify existing ones, or withdraw those that are no longer valid. These messages contain attributes that describe the characteristics of the route, such as the IP prefix and the list of ASs through which the traffic traverses.
Over time, certain BGP attributes become obsolete due to technological advancements or changes in operational needs. The IANA and IETF working groups are responsible for managing the creation and obsolescence of these attributes.
The presence of obsolete BGP attributes can lead to various problems, such as the following:
- Router incompatibility: Different software versions may interpret obsolete attributes differently, potentially leading to BGP sessions being dropped or the propagation of incorrect information.
- Security vulnerabilities: Obsolete attributes can be exploited by hackers to manipulate traffic or disrupt service.
- Unnecessary complexity: The persistence of obsolete attributes adds to the complexity of network management and makes it more difficult to troubleshoot.
The Case of the ‘Entropy Label’ Attribute
On 2 June 2023, a Brazilian Autonomous System (AS) announced one of its routes with attribute 28 (Entropy Label) enabled and marked as transitive, indicating that it should be propagated to other routers.
However, the BGP Entropy Label attribute caused BGP sessions to drop on routers beyond the AS’s direct peers. This issue was observed across different BGP implementations, where certain versions failed to handle this attribute correctly.
(Free access, no subscription required)
This flaw was classified as a vulnerability, and the need to maintain consistency in BGP implementations considering the state of obsolete attributes was highlighted to avoid similar disruptions in the future.
List of devices vulnerable to attacks with malformed BGP attributes:
- CVE-2023-4481 (Juniper)
- CVE-2023-38802 (FRR)
- CVE-2023-38283 (OpenBGPd)
- CVE-2023-40457 (EXOS)
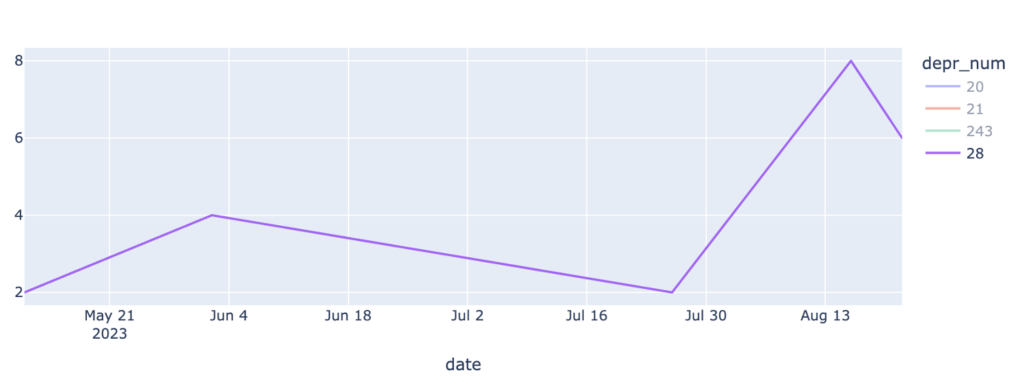
Analysis of Obsolete Attributes in the LACNIC Region
LACNIC conducted a study on the presence of obsolete attributes in BGP announcements observed by the LACNIC collector (RRC24) between October 2022 and October 2024. BVIEWS and UPDATES files were analyzed separately.
The views expressed by the authors of this blog are their own and do not necessarily reflect the views of LACNIC.
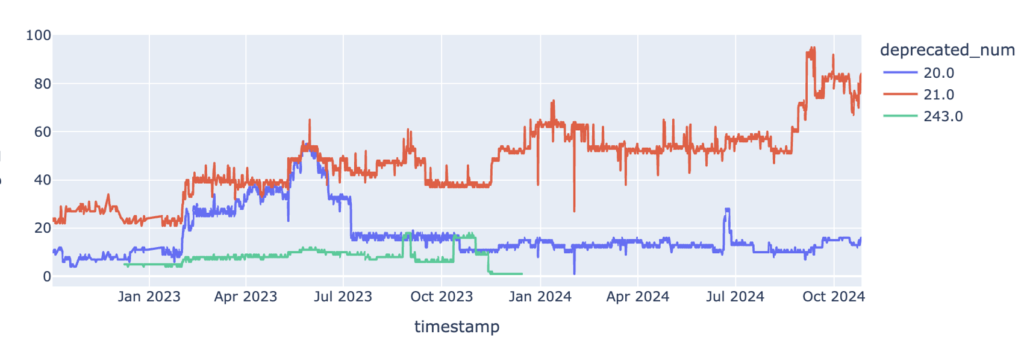
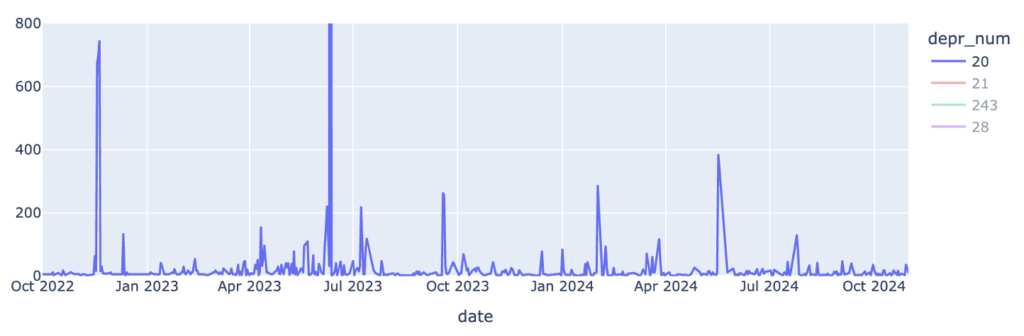
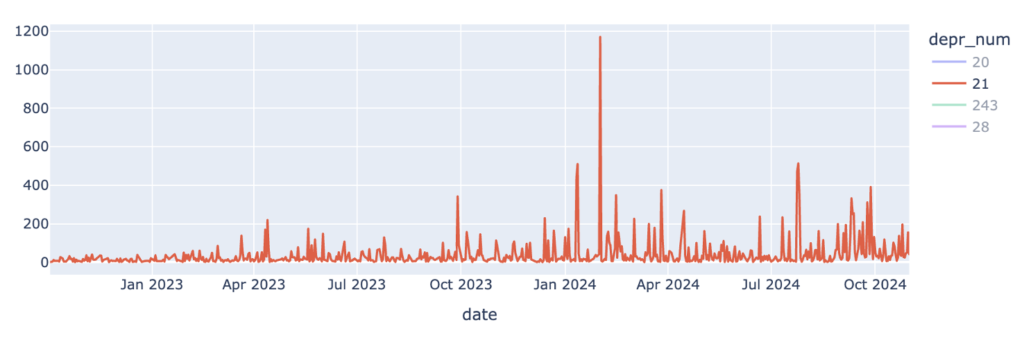
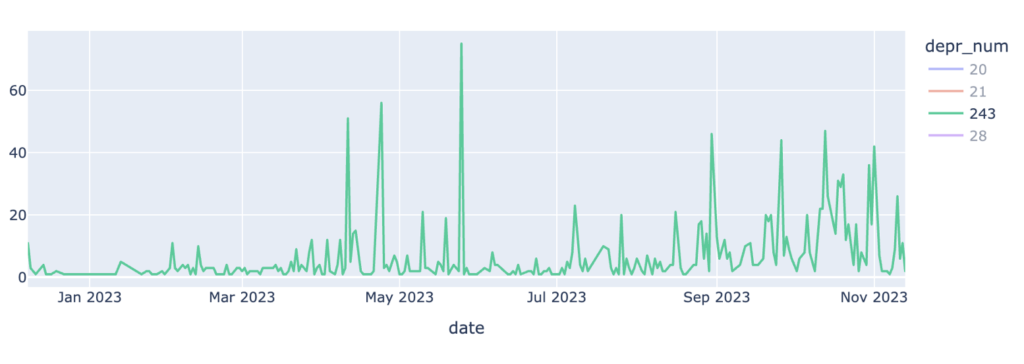
[…] LACNIC investigates the impact of outdated BGP attributes on regional networks, emphasising the need for modernised routing policies. LACNIC Blog […]